Prepared by:
HALBORN
Last Updated 05/30/2025
Date of Engagement: May 14th, 2025 - May 16th, 2025
Summary
100% of all REPORTED Findings have been addressed
All findings
9
Critical
0
High
0
Medium
2
Low
2
Informational
5
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Assessment summary
- 3. Test approach and methodology
- 4. Static analysis report
- 5. Risk methodology
- 6. Scope
- 7. Assessment summary & findings overview
- 8. Findings & Tech Details
- 8.1 Signature replay during unstaking
- 8.2 Unsafe token minting can lead to locked assets
- 8.3 Signature verification vulnerable to malleability
- 8.4 Zero amount stake allows for unlimited ticket token minting
- 8.5 Missing input validation
- 8.6 Missing events
- 8.7 Typo in function name
- 8.8 Use of revert strings instead of custom errors
- 8.9 Lack of named mapping
1. Introduction
Aria Protocol engaged Halborn to conduct a security assessment on their smart contracts beginning on May 14th, 2025 and ending on May 16th, 2025. The security assessment was scoped to the smart contracts provided to Halborn. Commit hashes and further details can be found in the Scope section of this report.
The Aria Protocol codebase in scope mainly consists of smart contracts implementing a staking mechanism for RWIP tokens with time-locked staking tickets and KYC verification for unstaking operations.
2. Assessment Summary
Halborn was provided 3 days for the engagement and assigned 1 full-time security engineer to review the security of the smart contracts in scope. The engineer is a blockchain and smart contract security expert with advanced penetration testing and smart contract hacking skills, and deep knowledge of multiple blockchain protocols.
The purpose of the assessment is to:
Identify potential security issues within the smart contracts.
Ensure that smart contract functionality operates as intended.
In summary, Halborn identified some improvements to reduce the likelihood and impact of risks, which were mostly addressed by the Aria Protocol team. The main ones are the following:
Include a nonce in the signed message that increments with each use.Replace the instance of _mint() with _safeMint() in the contract implementation to ensure recipients can properly handle ERC721 tokens.Replace the current signature verification with OpenZeppelin's ECDSA library which includes malleability protection.Add validation to ensure that staking amounts are greater than zero.
All addressed findings have been consolidated and incorporated into version v1.0.9, available in the following commit: https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/tree/c0a926fa1725b1bc03cca1bd8d70a5633ddcc061.
3. Test Approach and Methodology
Halborn performed a combination of manual review of the code and automated security testing to balance efficiency, timeliness, practicality, and accuracy in regard to the scope of this assessment. While manual testing is recommended to uncover flaws in logic, process, and implementation; automated testing techniques help enhance coverage of smart contracts and can quickly identify items that do not follow security best practices.
The following phases and associated tools were used throughout the term of the assessment:
Research into architecture, purpose and use of the platform.
Smart contract manual code review and walkthrough to identify any logic issue.
Thorough assessment of safety and usage of critical Solidity variables and functions in scope that could led to arithmetic related vulnerabilities.
Local testing with custom scripts (
Foundry).Fork testing against main networks (
Foundry).Static analysis of security for scoped contract, and imported functions (
Slither).
4. Static Analysis Report
4.1 Description
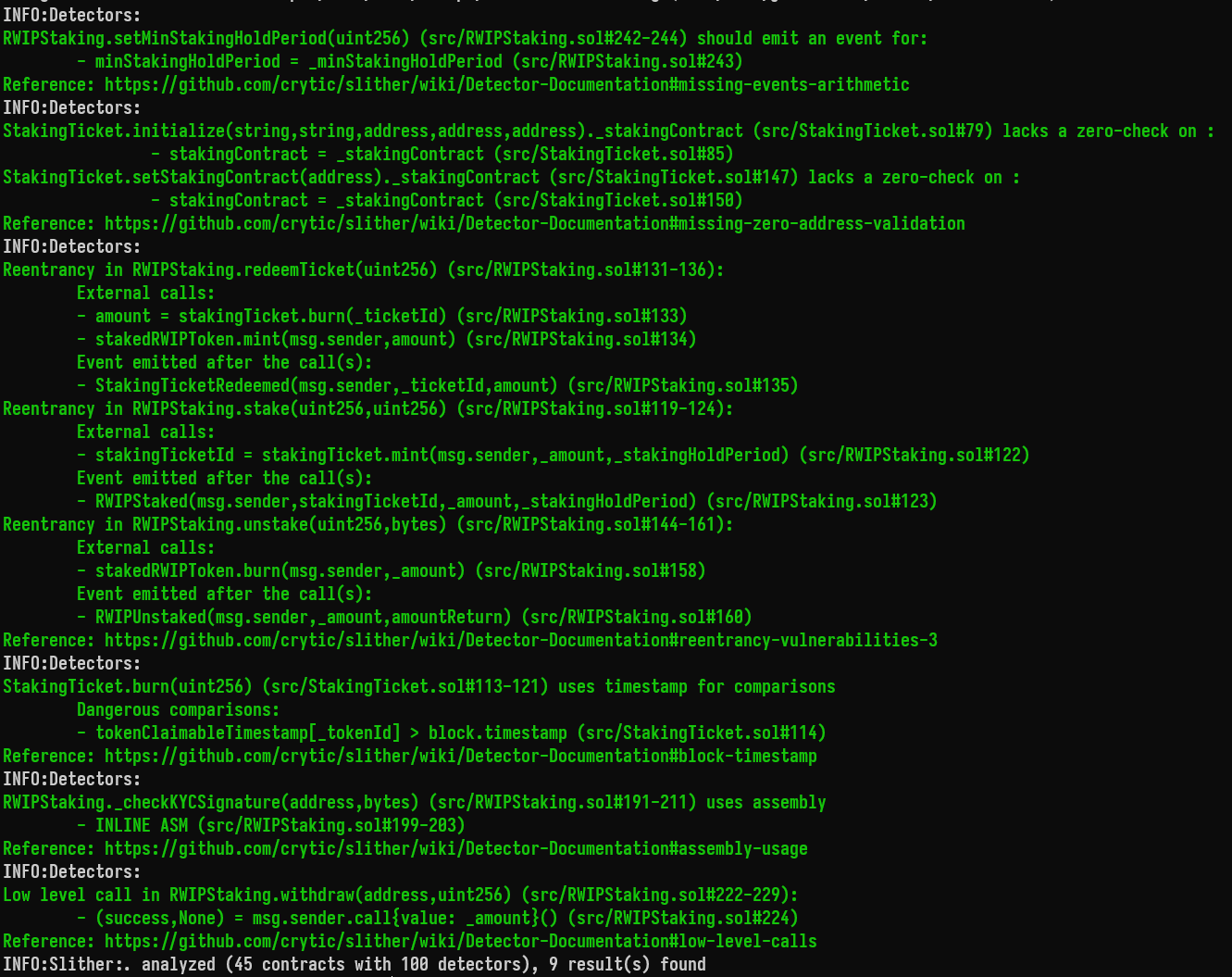
Halborn used automated testing techniques to enhance the coverage of certain areas of the smart contracts in scope. Among the tools used was Slither, a Solidity static analysis framework. After Halborn verified the smart contracts in the repository and was able to compile them correctly into their abis and binary format, Slither was run against the contracts. This tool can statically verify mathematical relationships between Solidity variables to detect invalid or inconsistent usage of the contracts' APIs across the entire code-base.
The security team assessed all findings identified by the Slither software, however, findings with related to external dependencies are not included in the below results for the sake of report readability.
4.2 Output
The findings obtained as a result of the Slither scan were reviewed, and some were not included in the report because they were determined as false positives.
5. RISK METHODOLOGY
5.1 EXPLOITABILITY
Attack Origin (AO):
Attack Cost (AC):
Attack Complexity (AX):
Metrics:
| EXPLOITABILITY METRIC () | METRIC VALUE | NUMERICAL VALUE |
|---|---|---|
| Attack Origin (AO) | Arbitrary (AO:A) Specific (AO:S) | 1 0.2 |
| Attack Cost (AC) | Low (AC:L) Medium (AC:M) High (AC:H) | 1 0.67 0.33 |
| Attack Complexity (AX) | Low (AX:L) Medium (AX:M) High (AX:H) | 1 0.67 0.33 |
5.2 IMPACT
Confidentiality (C):
Integrity (I):
Availability (A):
Deposit (D):
Yield (Y):
Metrics:
| IMPACT METRIC () | METRIC VALUE | NUMERICAL VALUE |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality (C) | None (C:N) Low (C:L) Medium (C:M) High (C:H) Critical (C:C) | 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 |
| Integrity (I) | None (I:N) Low (I:L) Medium (I:M) High (I:H) Critical (I:C) | 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 |
| Availability (A) | None (A:N) Low (A:L) Medium (A:M) High (A:H) Critical (A:C) | 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 |
| Deposit (D) | None (D:N) Low (D:L) Medium (D:M) High (D:H) Critical (D:C) | 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 |
| Yield (Y) | None (Y:N) Low (Y:L) Medium (Y:M) High (Y:H) Critical (Y:C) | 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1 |
5.3 SEVERITY COEFFICIENT
Reversibility (R):
Scope (S):
Metrics:
| SEVERITY COEFFICIENT () | COEFFICIENT VALUE | NUMERICAL VALUE |
|---|---|---|
| Reversibility () | None (R:N) Partial (R:P) Full (R:F) | 1 0.5 0.25 |
| Scope () | Changed (S:C) Unchanged (S:U) | 1.25 1 |
| Severity | Score Value Range |
|---|---|
| Critical | 9 - 10 |
| High | 7 - 8.9 |
| Medium | 4.5 - 6.9 |
| Low | 2 - 4.4 |
| Informational | 0 - 1.9 |
6. SCOPE
- contracts/rwip/staking/RWIPStaking.sol
- contracts/rwip/staking/StakedRWIP.sol
- contracts/rwip/staking/StakingTicket.sol
- https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/pull/44/commits/4db3df61201b6f279f42899ca3c7844906cf3f8b
- https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/pull/47/commits/e0854d66fa74b1061ba0682106c9629da8f1ea86
- https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/pull/45/commits/74ca8dd090a353922ddc24607b42d577a87201dc
- https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/pull/55/commits/612586a7cef867055b6f3c1d8e0cb9026a555daa
- https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/pull/55/commits/bfe98bdbadcbfb33b6e4affcbe9b191bb9f9a382
- https://github.com/AriaProtocol/main-contracts/pull/55/commits/0c53aaff2b9d83577382317a5e930e3062543449
7. Assessment Summary & Findings Overview
Critical
0
High
0
Medium
2
Low
2
Informational
5
| Security analysis | Risk level | Remediation Date |
|---|---|---|
| Signature replay during unstaking | Medium | Solved - 05/19/2025 |
| Unsafe token minting can lead to locked assets | Medium | Solved - 05/23/2025 |
| Signature verification vulnerable to malleability | Low | Solved - 05/23/2025 |
| Zero amount stake allows for unlimited ticket token minting | Low | Solved - 05/28/2025 |
| Missing input validation | Informational | Acknowledged - 05/28/2025 |
| Missing events | Informational | Partially Solved - 05/28/2025 |
| Typo in function name | Informational | Solved - 05/28/2025 |
| Use of revert strings instead of custom errors | Informational | Solved - 05/24/2025 |
| Lack of named mapping | Informational | Acknowledged - 05/28/2025 |
8. Findings & Tech Details
8.1 Signature replay during unstaking
//
Description
Proof of Concept
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
References
8.2 Unsafe token minting can lead to locked assets
//
Description
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
References
8.3 Signature verification vulnerable to malleability
//
Description
Proof of Concept
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
References
8.4 Zero amount stake allows for unlimited ticket token minting
//
Description
Proof of Concept
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
References
8.5 Missing input validation
//
Description
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
References
8.6 Missing events
//
Description
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
8.7 Typo in function name
//
Description
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
References
8.8 Use of revert strings instead of custom errors
//
Description
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
Remediation Hash
References
8.9 Lack of named mapping
//
Description
BVSS
Recommendation
Remediation Comment
References
Halborn strongly recommends conducting a follow-up assessment of the project either within six months or immediately following any material changes to the codebase, whichever comes first. This approach is crucial for maintaining the project’s integrity and addressing potential vulnerabilities introduced by code modifications.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Assessment summary
- 3. Test approach and methodology
- 4. Static analysis report
- 5. Risk methodology
- 6. Scope
- 7. Assessment summary & findings overview
- 8. Findings & Tech Details
- 8.1 Signature replay during unstaking
- 8.2 Unsafe token minting can lead to locked assets
- 8.3 Signature verification vulnerable to malleability
- 8.4 Zero amount stake allows for unlimited ticket token minting
- 8.5 Missing input validation
- 8.6 Missing events
- 8.7 Typo in function name
- 8.8 Use of revert strings instead of custom errors
- 8.9 Lack of named mapping
// Download the full report
Staking Contracts
* Use Google Chrome for best results
** Check "Background Graphics" in the print settings if needed
